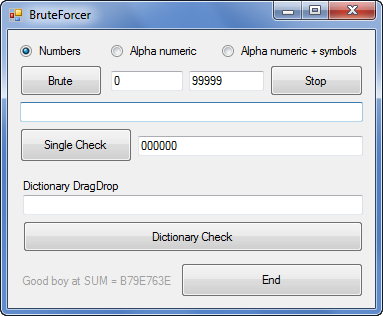
Aviso: Este crackme forma parte de una serie de pruebas de Yoire.com que todavía está en activo. Lo ético si continuas leyendo este manual es que no utilices la respuesta para completar la prueba sin esfuerzo. 😉
Analizando
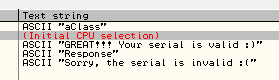
Abrimos el crackme con Ollydbg y vamos a las referenced strings.
Pinchamos sobre cualquiera.
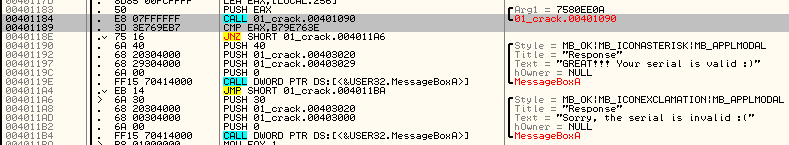
Vemos un «Call» donde seguramente se generará un SUM en función del serial metido ya que después del Call vemos una comprobación contra «B79E763E» lo que nos da una pista de que vamos a tener que utilizar fuerza bruta para llegar a ese valor. Vamos a explorar el Call.
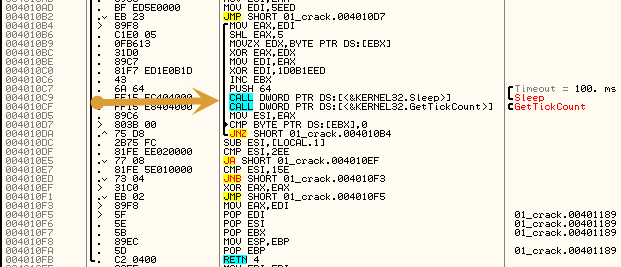
Lo que resalto con la flecha son una par de Calls que podemos NOPear ya que lo único que hacen es ralentizar la generación del SUM.
A continuación vamos a analizar el algoritmo de generación del SUM.
MOV EDI,5EED - EDI = 5EED JMP SHORT 01_crack.004010D7 /MOV EAX,EDI <----Bucle |SHL EAX,5 - 5EED * 32 = BDDA0 |MOVZX EDX,BYTE PTR DS:[EBX] - Coge el dígito |XOR EAX,EDX - BDDA0 XOR digito |MOV EDI,EAX |XOR EDI,1D0B1EED - XOR 1D0B1EED |INC EBX |.. |MOV ESI,EAX CMP BYTE PTR DS:[EBX],0 JNZ SHORT 01_crack.004010B4 - Bucle ---->
Para un serial de tres dígitos la secuencia sería esta (valores en hexadecimal):
1º Digit —> BDDA0 XOR 1D0B1EED XOR 1ºDigit XOR 1D0B1EED = Temp
2º Digit —> Temp = Temp * 20 Xor 1D0B1EED XOR 2ºDigit
3º Digit —> Temp = Temp * 20 Xor 1D0B1EED XOR 3ºDigit
…
CMP Temp, B79E763E
2º Digit —> Temp = Temp * 20 Xor 1D0B1EED XOR 2ºDigit
3º Digit —> Temp = Temp * 20 Xor 1D0B1EED XOR 3ºDigit
…
CMP Temp, B79E763E
Aplicando Fuerza Bruta
La creación del «BruteForcer» os la dejo a vosotros. Aquí teneis un fragmento hecho en VB.Net.
Dim temp As Long Dim temp2 As String Dim letter As Integer Dim brute As String brute = TextBox4.Text temp = 0 temp = Asc(Mid(brute, 1, 1)) Xor 487268077 Xor 777632 temp2 = Hex(temp) temp2 = Microsoft.VisualBasic.Right(temp2, 8) temp = Convert.ToUInt64(temp2, 16) For i = 2 To Len(brute) letter = Asc(Mid(brute, i, 1)) temp = temp * 32 temp2 = Hex(temp) temp2 = Microsoft.VisualBasic.Right(temp2, 8) temp = Convert.ToUInt64(temp2, 16) temp = temp Xor 487268077 temp2 = Hex(temp) temp2 = Microsoft.VisualBasic.Right(temp2, 8) temp = Convert.ToUInt64(temp2, 16) temp = temp Xor letter ' temp2 = Hex(temp) Next